Zero-calorie Sweetener Natural Erythritol Powder
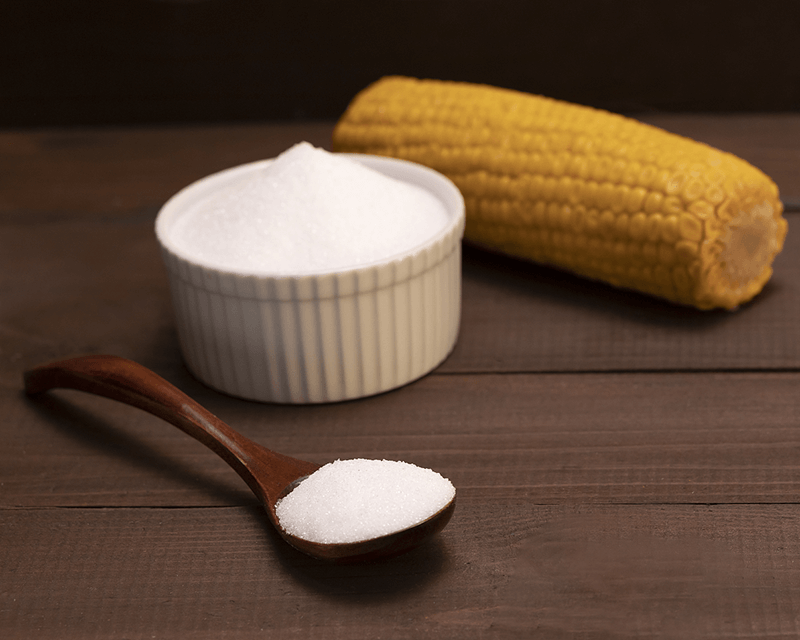
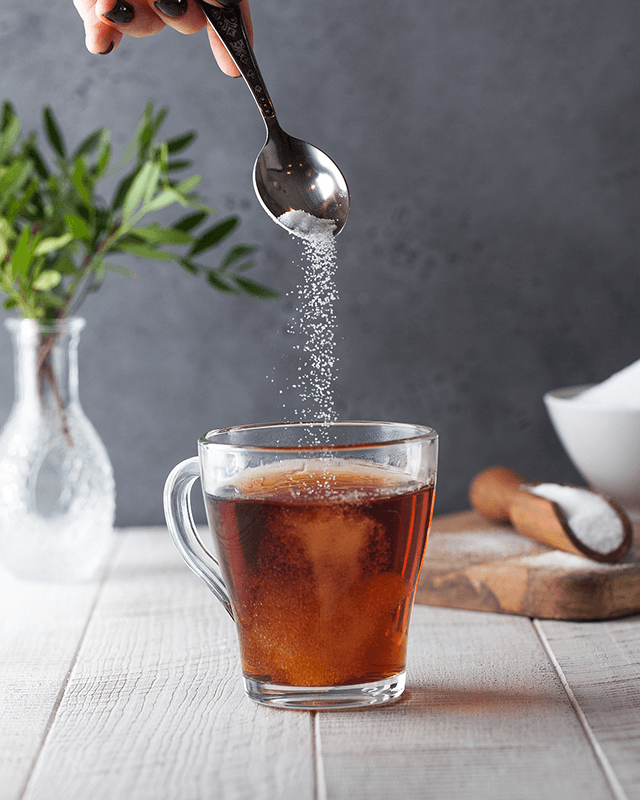
Natural erythritol powder is a sugar substitute and zero-calorie sweetener that is derived from natural sources such as fruits and fermented foods(like corn). It belongs to a class of compounds called sugar alcohols. Erythritol has a taste and texture similar to sugar but provides fewer calories and does not raise blood sugar levels, making it a popular choice for those following low-calorie or sugar-restricted diets.
Erythritol is also known as a non-nutritive sweetener because it is not metabolized by the body like traditional sugars. This means that it passes through the digestive system largely unchanged, resulting in minimal impact on blood sugar levels and insulin response.
One of the key advantages of natural erythritol powder is that it provides sweetness without any aftertaste that is commonly associated with other sugar substitutes. It can be used in various food and beverage applications, including baking, cooking, and sweetening hot or cold drinks.
It is important to note that while erythritol is generally safe for consumption, excessive intake may cause digestive issues such as bloating or diarrhea in some individuals. As with any alternative sweetener, it is recommended to use erythritol in moderation and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any specific dietary or health concerns.
| Product | Erythritol | Specification | Net 25kg |
| Test Basis | GB26404 | Expiry date | 20230425 |
| Test Items | Specification | Test result | Conclusion |
| Color | White | White | Pass |
| Taste | Sweet | Sweet | Pass |
| Character | Crystalline powder or particle | Crystalline powder | Pass |
| Impurity | No visible impurities, no foreign matter |
No foreign matter | Pass |
| Assay (dry basis),% | 99.5~100.5 | 99.9 | Pass |
| Drying loss,% ≤ | 0.2 | 0.1 | Pass |
| Ash,% ≤ | 0.1 | 0.03 | Pass |
| Reducing sugars,% ≤ | 0.3 | <0.3 | Pass |
| w/% Ribitol&glycerol,% ≤ | 0.1 | <0.1 | Pass |
| pH value | 5.0~7.0 | 6.4 | Pass |
| (As)/(mg/kg) Total arsenic | 0.3 | <0.3 | Pass |
| (Pb)/(mg/kg) Lead | 0.5 | Not detected | Pass |
| /(CFU/g) Total plate count | ≤100 | 50 | Pass |
| (MPN/g) Coliform | ≤3.0 | <0.3 | Pass |
| /(CFU/g) Mold and yeast | ≤50 | 20 | Pass |
| Conclusion | Complies with requirements of food grade. | ||
Zero-calorie sweetener: Natural erythritol powder provides sweetness without any calories, making it an ideal sugar substitute for those watching their calorie intake.
Derived from natural sources: Erythritol is derived from natural sources such as fruits and fermented foods, making it a more natural and healthier alternative to artificial sweeteners.
Does not raise blood sugar levels: Erythritol does not cause a spike in blood sugar levels, making it suitable for individuals with diabetes or those following a low-carb or low-sugar diet.
No aftertaste: Unlike some other sugar substitutes, erythritol does not leave a bitter or artificial aftertaste in the mouth. It provides a clean and similar taste to sugar.
Versatile: Natural erythritol powder can be used in a variety of food and beverages, including baking, cooking, and sweetening hot or cold drinks.
Tooth-friendly: Erythritol does not promote tooth decay and is considered tooth-friendly, making it an excellent choice for oral health.
Suitable for restrictive diets: Erythritol is often used by individuals following keto, paleo, or other low-sugar diets as it provides a sweet taste without the negative effects of sugar.
Digestive friendly: While sugar alcohols are sometimes associated with digestive issues, erythritol is generally well-tolerated and less likely to cause bloating or digestive discomfort compared to other sugar alcohols.
Overall, natural erythritol powder is a versatile and healthier alternative to sugar, providing sweetness without adding calories or raising blood sugar levels.
Natural erythritol powder has several health benefits when used as a sugar substitute:
Low in calories: Erythritol is a zero-calorie sweetener, meaning it provides sweetness without contributing to the caloric content of foods or beverages. This makes it a suitable option for individuals looking to reduce their calorie intake and manage their weight.
Does not raise blood sugar levels: Unlike regular sugar, erythritol does not significantly impact blood sugar levels or insulin response. This makes it an excellent choice for those with diabetes or individuals following a low-carbohydrate or ketogenic diet.
Tooth-friendly: Erythritol is not readily fermented by the bacteria in the mouth, which means it does not contribute to tooth decay or cavities. In fact, some studies suggest that erythritol may have a positive effect on dental health by reducing plaque formation and the risk of dental caries.
Suitable for individuals with digestive sensitivities: Erythritol is generally well-tolerated by most people and does not commonly cause digestive issues or gastrointestinal discomfort. Unlike some other sugar alcohols, such as maltitol or sorbitol, erythritol is less likely to cause bloating or diarrhea.
Glycemic index (GI) value: Erythritol has a glycemic index value of zero, meaning it has no impact on blood sugar levels. This makes it a suitable sweetener for individuals following a low-GI diet or those looking to control their blood sugar levels.
It is important to note that while erythritol is generally recognized as safe and considered a healthy sugar alternative, it should still be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. As with any dietary change, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice.
Natural erythritol powder has a wide range of applications across various fields. Some common application fields include:
Food and beverage industry: Natural erythritol powder is often used as a sweetener in food and beverage products such as baked goods, candies, chewing gums, beverages, and desserts. It provides sweetness without adding calories and has a taste similar to sugar.
Dietary supplements: It is also commonly used in dietary supplements, such as protein powders and meal replacement shakes, to provide a sweet taste without adding excessive calories or sugar.
Personal care products: Natural erythritol powder can be found in toothpaste, mouthwash, and other oral care products. Its tooth-friendly properties make it an ideal ingredient for oral health products.
Pharmaceuticals: It is used as an excipient in certain pharmaceutical formulations, helping to improve the taste and stability of medications.
Cosmetics: Erythritol is sometimes used in cosmetics and skincare products as a humectant, helping to attract and retain moisture in the skin. It can also provide a pleasant texture and help to improve the overall feel and sensory experience of cosmetic products.
Animal feed: In the livestock industry, erythritol can be used as an ingredient in animal feed as a source of energy or a sweetening agent.
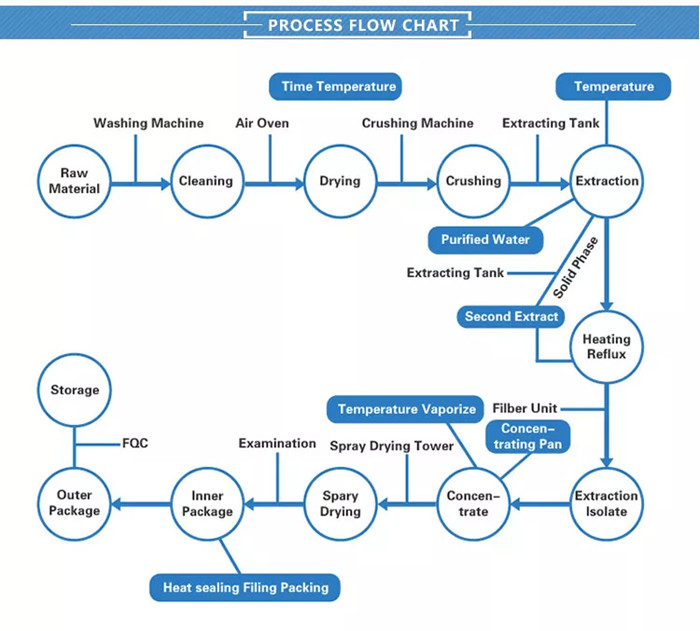
The production process of natural erythritol powder involves several steps:
Fermentation: Erythritol is derived through a process called microbial fermentation. A natural sugar, typically derived from corn or wheat starch, is fermented using a specific strain of yeast or bacteria. The most common yeast used is Moniliella pollinis or Trichosporonoides megachiliensis. During fermentation, the sugar is converted into erythritol.
Purification: After fermentation, the mixture is filtered to remove the yeast or bacteria used in the process. This helps separate the erythritol from the fermentation medium.
Crystallization: The extracted erythritol is then dissolved in water and heated to form a concentrated syrup. Crystallization is induced by slowly cooling the syrup, encouraging the erythritol to form crystals. The cooling process can take several hours, allowing for the growth of larger crystals.
Separation and drying: Once the erythritol crystals have formed, they are separated from the remaining liquid through a centrifuge or filtration process. The resulting wet erythritol crystals are then dried to remove any remaining moisture. Drying can be accomplished using techniques such as spray drying or vacuum drying, depending on the desired particle size and moisture content of the final product.
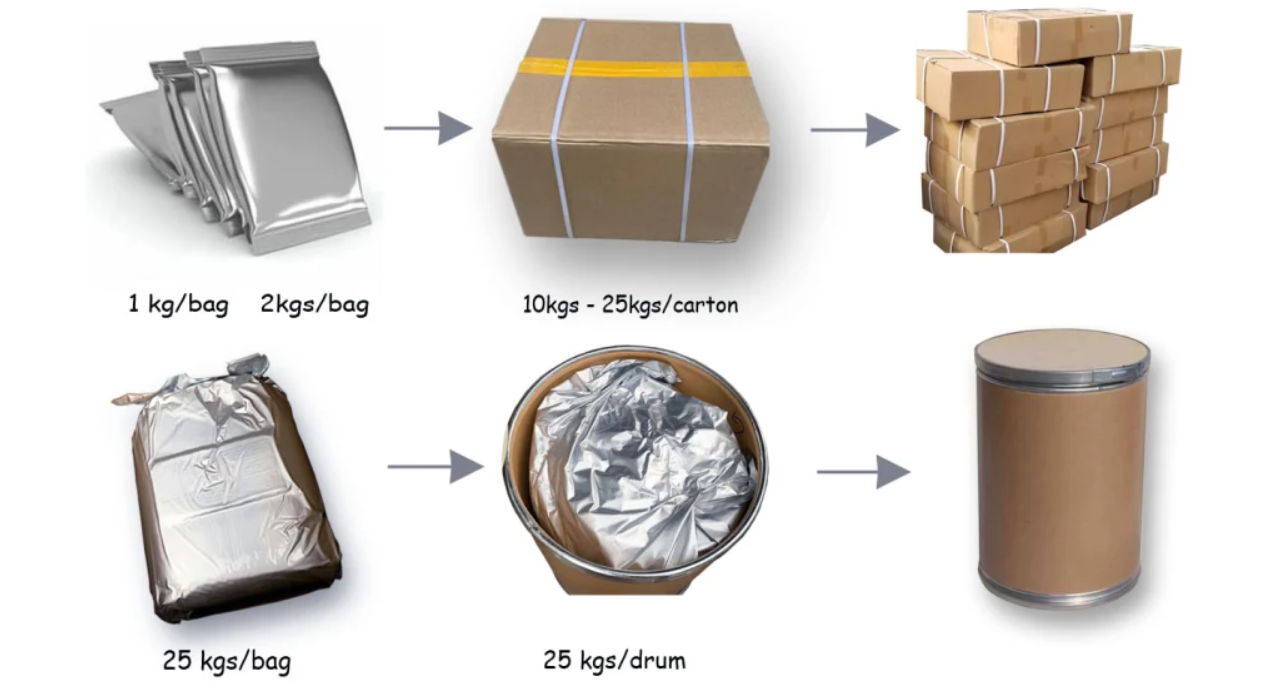
Grinding and packaging: The dried erythritol crystals are ground into a fine powder using a milling machine. The powdered erythritol is then packaged in airtight containers or bags to maintain its quality and prevent moisture absorption.
Express
Under 100kg, 3-5Days
Door to door service easy to pick up the goods
By Sea
Over300kg, Around 30 Days
Port to port service professional clearance broker needed
By Air
100kg-1000kg, 5-7Days
Airport to airport service professional clearance broker needed

Zero-calorie Sweetener Natural Erythritol Powder is certified by ISO, HALAL, KOSHER, and HACCP certificates.

While natural erythritol powder is generally considered safe and has several advantages, it also has a few potential disadvantages, including:
Cooling effect: Erythritol has a cooling effect on the palate, similar to mint or menthol. This cooling sensation can be unpleasant for some individuals, particularly in higher concentrations or when used in certain foods or beverages.
Digestive issues: Erythritol is not fully absorbed by the body and can pass through the gastrointestinal tract largely unchanged. In large quantities, it may lead to digestive issues such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea, especially for people who are sensitive to sugar alcohol.
Reduced sweetness: Compared to table sugar, erythritol is less sweet. To provide the same level of sweetness, you may need to use a larger amount of erythritol, which can alter the texture and taste of certain recipes.
Possible laxative effect: Although erythritol generally has a minimal laxative effect compared to other sugar alcohols, consuming large amounts in a short period may still cause digestive discomfort or laxative effects, especially for individuals who are more sensitive.
Possible allergic reactions: While rare, there have been reported cases of erythritol allergy or sensitivity. People with known allergies or sensitivities to other sugar alcohols, such as xylitol or sorbitol, may be at an increased risk of allergic reactions to erythritol.
It is important to note that individual reactions to erythritol can vary, and some people may tolerate it better than others. If you have any concerns or specific health conditions, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before consuming erythritol or any other sugar substitute.
Both natural erythritol powder and natural sorbitol powder are sugar alcohols that are commonly used as sugar substitutes. However, there are some differences between the two:
Sweetness: Erythritol is approximately 70% as sweet as table sugar, while sorbitol is about 60% as sweet. This means that you may need to use slightly more erythritol than sorbitol to achieve the same level of sweetness in recipes.
Calories and glycemic impact: Erythritol is virtually calorie-free and has no impact on blood sugar levels, making it a popular choice for those on low-calorie or low-carb diets. Sorbitol, on the other hand, contains roughly 2.6 calories per gram and has a low glycemic index, meaning it can still influence blood sugar levels, although to a lesser extent than regular sugar.
Digestive tolerance: Erythritol is usually well-tolerated by most people and has minimal digestive side effects, such as bloating or diarrhea, even when consumed in moderate to high amounts. However, sorbitol can have a laxative effect and may cause gastrointestinal issues, especially when consumed in large quantities.
Cooking and baking properties: Both erythritol and sorbitol can be used in cooking and baking. Erythritol tends to have better heat stability and does not ferment or caramelize easily, making it a suitable choice for high-temperature baking. Sorbitol, on the other hand, may have a slight impact on texture and taste due to its lower sweetness and higher moisture content.
Availability and cost: Both erythritol and sorbitol can be found in various stores and online retailers. However, the cost and availability may vary depending on your location and specific brands.
Ultimately, the choice between natural erythritol powder and natural sorbitol powder depends on individual preferences, dietary considerations, and intended use. It may be useful to experiment with both to determine which one suits your needs and tastes better.