Natural Food Additive Sorbitol Powder
Natural food additive sorbitol powder is a sweetener and sugar substitute that is derived from fruits and plants, such as corn or berries. It is a type of sugar alcohol and is commonly used in a variety of food and beverage products.
Sorbitol is known for its sweet taste, similar to sugar, but with fewer calories. It can be used in various applications, including baked goods, candies, chewing gum, dietary supplements, and diabetic-friendly products.
One of the main advantages of sorbitol powder as a food additive is its ability to provide sweetness without causing a significant increase in blood sugar levels. This makes it suitable for individuals who need to control their blood sugar, such as diabetics.
Additionally, sorbitol has a lower glycemic index compared to sugar, which means it has a slower and more gradual impact on blood sugar levels. It is also a sugar alternative for those looking to reduce their overall sugar intake and manage their weight.
Sorbitol is often used as a bulking agent or filler in various food products, as it can add volume and texture while enhancing sweetness. It also helps retain moisture in baked goods, preventing them from drying out.
Furthermore, sorbitol powder is considered safe for consumption when used in moderate amounts. However, excessive consumption can have a laxative effect, as sugar alcohols are not fully absorbed by the body and can ferment in the intestines.
In summary, Natural sorbitol powder is a natural food additive that provides sweetness with fewer calories and a lower impact on blood sugar levels. It is commonly used in various food and beverage products as a sugar substitute and can be a suitable option for individuals with specific dietary needs.
Description of Sorbitol:
| Product Name: | Sorbitol |
| Synonyms: | D-Glucitol (D-Sorbitol);Yamanashi sugar alcohol;Yamanashi sugar alcohol solution;Sorbitol 50-70-4;SORBITOL;Parteck SI 200 (Sorbitol);Parteck SI 400 LEX (Sorbitol) |
| CAS: | 50-70-4 |
| MF: | C6H14O6 |
| MW: | 182.17 |
| EINECS: | 200-061-5 |
| Product Categories: | RESULAX;Food additives and Sweeteners;Biochemistry;Glucose;Sugar Alcohols;Inhibitors;Sugars;Food additives;Dextrins,Sugar & Carbohydrates;Food & Flavor Additives |
| Mol File: | 50-70-4.mol |
Specification:
| Product name | Sorbitol 70% | Manu date | Oct.15,2022 | |||
| Inspection date | Oct.15.2020 | Expiry date | Apr.01.2023 | |||
| inspection standard | GB 7658--2007 | |||||
| index | requirement | results | ||||
| Appearance | Transparent, sweety, viscidity | qualified | ||||
| Dry solids,% | 69.0-71.0 | 70.31 | ||||
| Sorbitol content,% | ≥70.0 | 76.5 | ||||
| Ph value | 5.0-7.5 | 5.9 | ||||
| Relative density(d2020) | 1.285-1.315 | 1.302 | ||||
| Dextrose,% | ≤0.21 | 0.03 | ||||
| Total dextrose,% | ≤8.0 | 6.12 | ||||
| Residual after burning,% | ≤0.10 | 0.04 | ||||
| Heavy metal,% | ≤0.0005 | <0.0005 | ||||
| Pb(base on pb),% | ≤0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||
| As (based on As),% | ≤0.0002 | <0.0002 | ||||
| Chloride(base on Cl),% | ≤0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Sulphate(base on SO4),% | ≤0.005 | <0.005 | ||||
| Nickel(base on Ni),% | ≤0.0002 | <0.0002 | ||||
| Assess | qualified with the standard | |||||
| Remarks | This report is a response to goods of this batch | |||||
Natural Sweetener: Natural sorbitol, also known as a sugar alcohol, is commonly used as a sweetener in various food and beverage products. It provides a sweet taste similar to sucrose (table sugar) without the high-calorie content.
Low Glycemic Index: Sorbitol has a low glycemic index, which means it does not cause a sharp increase in blood sugar levels when consumed. This makes it a suitable option for individuals on low-sugar or diabetic diets.
Sugar Substitute: it can be used as a sugar substitute in different recipes and food applications, including baking, confectionery, and beverages. It can help reduce the total sugar content of products without compromising taste.
Humectant and Moisturizer: Sorbitol acts as a humectant, helping to retain moisture and prevent drying out. This property makes it a common ingredient in personal care products such as lotions, creams, and toothpaste.
Non-cariogenic: Unlike regular sugar, sorbitol does not promote tooth decay or cavities. It is non-cariogenic, making it a suitable ingredient for oral hygiene products like sugar-free gum, mouthwash, and dental care items.
Solubility: it has excellent solubility in water, allowing it to blend easily in liquid formulations. This feature makes it convenient to incorporate into a wide range of food and beverage products.
Synergistic Effects: Sorbitol has synergistic effects with other sweeteners like sucralose and stevia. It enhances the sweetness profile and can be combined with these sweeteners to create sugar-free or reduced-sugar products.
Stable at High Temperatures: It maintains its stability and sweetness even at high temperatures, making it suitable for use in baking and cooking applications.
Preservative Properties: Sorbitol has preservative properties that can help extend the shelf life of certain food products, preventing spoilage and microbial growth.
Low-Calorie: Compared to regular sugar, sorbitol has fewer calories per gram. This can be beneficial for individuals looking to reduce their calorie intake or manage their weight.
Low Calorie: Sorbitol has fewer calories compared to regular sugar, making it a suitable option for individuals looking to manage their weight or reduce calorie intake.
Diabetic-Friendly: It has a low glycemic index, meaning it does not cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This makes it a suitable choice for individuals with diabetes or those looking to regulate their blood sugar levels.
Digestive Health: It acts as a mild laxative and can help relieve constipation by drawing water into the intestines, and promoting bowel movements.
Dental Health: It is non-cariogenic, meaning it does not promote tooth decay. It can be used in sugar-free chewing gums, candies, and oral hygiene products to reduce the risk of cavities and promote dental health.
Sugar Substitute: It can be used as a sugar substitute in various food and beverage products. Using sorbitol instead of regular sugar can help reduce overall sugar intake, which is beneficial for those looking to manage their sugar consumption.
Humectant and Moisturizing Properties: It acts as a humectant, helping to retain moisture in products. This property makes it a common ingredient in personal care products like creams, lotions, and toothpaste, contributing to their moisturizing effects.
Gluten-Free and Allergen-Free: It is gluten-free and does not contain common allergens such as wheat, dairy, nuts, or soy, making it safe for individuals with specific dietary restrictions or allergies.
Prebiotic Properties: Some studies suggest that sorbitol may act as a prebiotic, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. A healthy gut microbiota is essential for digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall digestive health.
Natural Sorbitol Powder has several applications across various fields. Here are some common application fields:
Food and Beverage Industry: It is widely used as a sugar substitute in many food and beverage products. It provides sweetness without the same calorie content as regular sugar. It can be found in products like sugar-free candies, chewing gum, baked goods, frozen desserts, and beverages.
Pharmaceutical Industry: It is a common ingredient in pharmaceutical formulations. It is often used as a filler or diluent in tablets, capsules, and syrups. It helps to improve the consistency, stability, and palatability of medications.
Personal Care Products: It can be found in various personal care products such as toothpaste, mouthwash, and cosmetics. It is used as a humectant, which helps to retain moisture and prevent drying out of the products.
Medical and Oral Care Products: It is commonly used as an ingredient in medical products like cough syrups, throat lozenges, and mouthwashes. It provides a soothing effect and can help relieve throat irritation.
Cosmetics and Skincare Products: It can be found in skincare products like moisturizers, lotions, and creams. It acts as a humectant, helping to attract and retain moisture in the skin, keeping it hydrated and supple.
Nutraceuticals: It is used in nutraceutical products like dietary supplements and functional foods. It can provide sweetness while also acting as a bulking agent, contributing to the overall texture and palatability of these products.
It's important to note that sorbitol powder can have a laxative effect in large quantities, so it's essential to use it in moderation and follow recommended dosage guidelines.
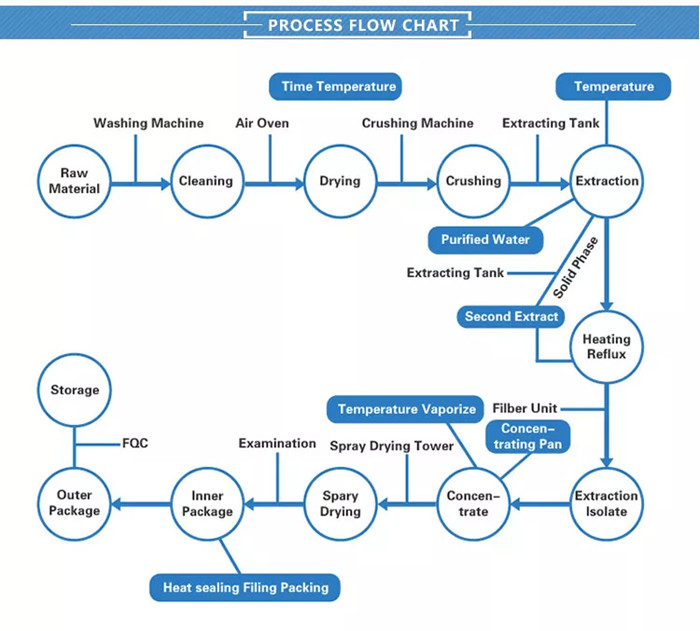
The production process of natural sorbitol powder involves several steps:
Raw Material Preparation: The process starts with selecting and preparing the raw materials. Natural sorbitol can be derived from various sources like fruits (such as apples or pears) or corn. These raw materials are washed, peeled, and chopped into smaller pieces.
Extraction: The chopped fruits or corn are then subjected to extraction to obtain the sorbitol solution. Various extraction methods can be used, including water extraction or enzymatic hydrolysis. In the water extraction method, the raw material is soaked in water, and heat is applied to extract the sorbitol. Enzymatic hydrolysis involves using specific enzymes to break down the starch present in corn into sorbitol.
Filtration and Purification: The extracted sorbitol solution is filtered to remove any solid particles or impurities. It may undergo further purification processes, such as ion-exchange chromatography or activated carbon filtration, to remove any remaining impurities, colorants, or odor-causing substances.
Concentration: The filtrate containing sorbitol is concentrated to increase the sorbitol content and remove excess water. This is typically done using processes like evaporation or membrane filtration. Evaporation involves heating the solution to evaporate the water content, while membrane filtration uses selectively permeable membranes to separate water molecules from sorbitol molecules.
Crystallization: The concentrated sorbitol solution is cooled down gradually, leading to the formation of sorbitol crystals. Crystallization helps separate the sorbitol from other components of the solution. The crystals are typically removed using filtration or centrifugation.
Drying: The sorbitol crystals are further dried to remove any remaining moisture and obtain the desired moisture content. This can be achieved using techniques like spray drying, vacuum drying, or fluidized bed drying. Drying ensures the stability and long shelf life of the sorbitol powder.
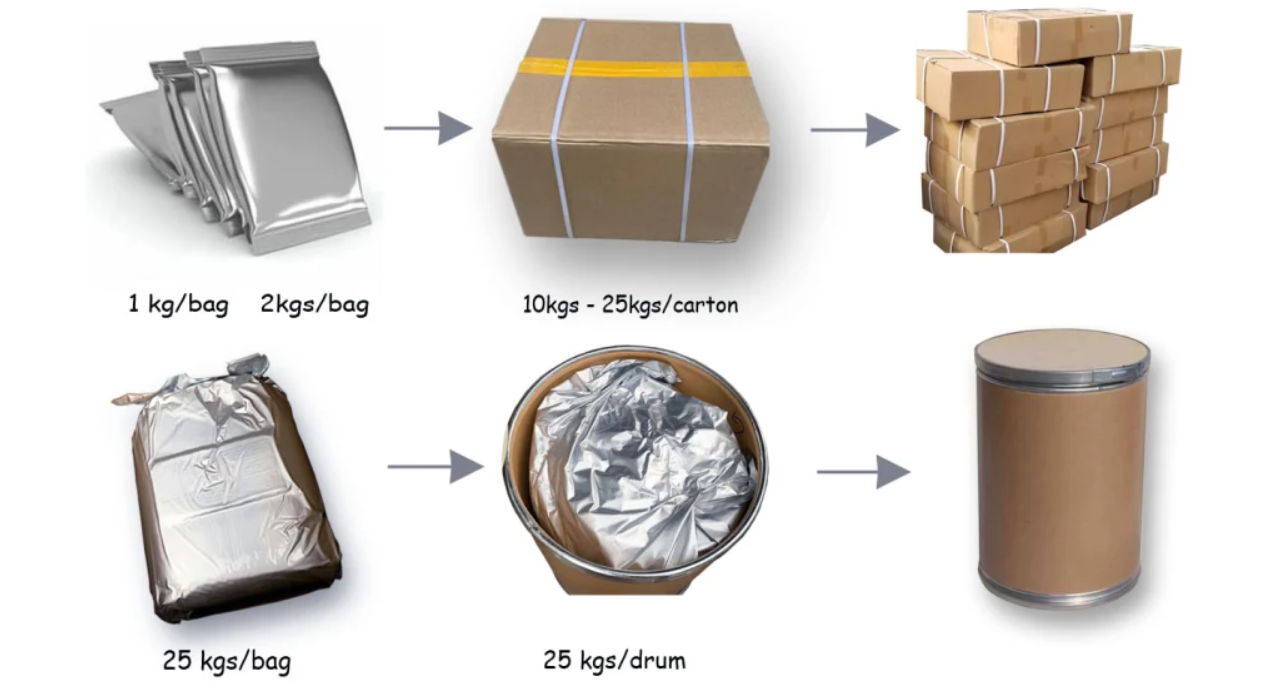
Milling and Packaging: The dried sorbitol crystals are milled into a fine powder to obtain the desired particle size. This improves the flowability and ease of handling. The powdered sorbitol is then packaged in suitable containers or bags, ensuring proper labeling and storage conditions.
It's important to note that the specific details of the production process can vary depending on the manufacturer and the source of natural sorbitol. Good manufacturing practices (GMP) should be followed to ensure the quality, safety, and consistency of the natural sorbitol powder product.
Express
Under 100kg, 3-5Days
Door to door service easy to pick up the goods
By Sea
Over300kg, Around 30 Days
Port to port service professional clearance broker needed
By Air
100kg-1000kg, 5-7Days
Airport to airport service professional clearance broker needed

Natural Sorbitol Powder is certified by ISO, HALAL, KOSHER, and HACCP certificates.

There are several natural food ingredients that can be used as sweeteners. Here are some examples:
Stevia: Stevia is a plant-based sweetener extracted from the leaves of the stevia plant. It is known for its intense sweetness and can be used as a zero-calorie alternative to sugar.
Honey: Honey is a natural sweetener produced by bees from flower nectar. It contains various enzymes, antioxidants, and trace minerals. However, it is high in calories and should be consumed in moderation.
Maple Syrup: Maple syrup is derived from the sap of maple trees. It adds a unique flavor and sweetness to dishes and can be used as a natural alternative to refined sugar.
Molasses: Molasses is a thick, syrupy byproduct of the sugar cane refining process. It has a rich, dark flavor and is often used in baking or as a flavor enhancer.
Coconut Sugar: Coconut sugar is made from the sap of coconut palm flowers. It has a caramel-like flavor and can be used as a substitute for regular sugar in various recipes.
Monk Fruit Extract: Monk fruit extract is extracted from the fruit of the monk fruit plant. It is a natural, zero-calorie sweetener that is significantly sweeter than sugar.
Date Sugar: Date sugar is made by drying and grinding dates into a powdered form. It retains the natural fiber and nutrients of dates and can be used as a natural sweetener in baking.
Agave Nectar: Agave nectar is derived from the agave plant and has a similar consistency to honey. It is sweeter than sugar and can be used as a substitute in beverages, baking, and cooking.
It's worth noting that while these natural sweeteners can be healthier alternatives to refined sugar, they should still be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
While Natural Sorbitol Powder has several beneficial uses, it also has some potential disadvantages. Here are a few to consider:
Laxative Effect: Sorbitol is a sugar alcohol that can have a laxative effect when consumed in large quantities. Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, including diarrhea, bloating, and gas, if they consume excessive amounts of sorbitol. It is important to use it in moderation and follow recommended dosage guidelines.
Digestive Sensitivity: Some individuals may be more sensitive to sorbitol than others, experiencing digestive issues even with smaller amounts. People with certain gastrointestinal conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), may find sorbitol difficult to tolerate.
Calorie Content: While sorbitol is often used as a sugar substitute due to its lower calorie content, it is not entirely calorie-free. It still contains some calories, approximately 2.6 calories per gram, although this is significantly lower than regular sugar. Individuals on strict low-calorie diets should be mindful of sorbitol's calorie content.
Potential Allergies or Sensitivities: Although rare, some individuals may have allergies or sensitivities to sorbitol. If you have experienced any allergic reactions or sensitivities to sorbitol or other sugar alcohols in the past, it is best to avoid using products containing sorbitol.
Dental Concerns: While sorbitol is often used in oral care products, it is important to note that excessive consumption of sorbitol-containing products can contribute to tooth decay. Sorbitol is less prone to promoting tooth decay than regular sugar, but frequent exposure to high concentrations of sorbitol can still have an impact on dental health.
It is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional or a dietician before incorporating any new ingredient or product into your diet or routine, especially if you have specific health concerns.






















